It’s easy for them to say hair-fall ain’t a big deal who are blessed with a glorious mane! However, for the ones who are quite terrified to put a comb through their hair because of hair-fall, the discussion of balding is no joke. Though most people think of balding as something that strikes in middle age, the truth is that, hair loss often starts early and develops slowly – especially in men.
What is early balding?
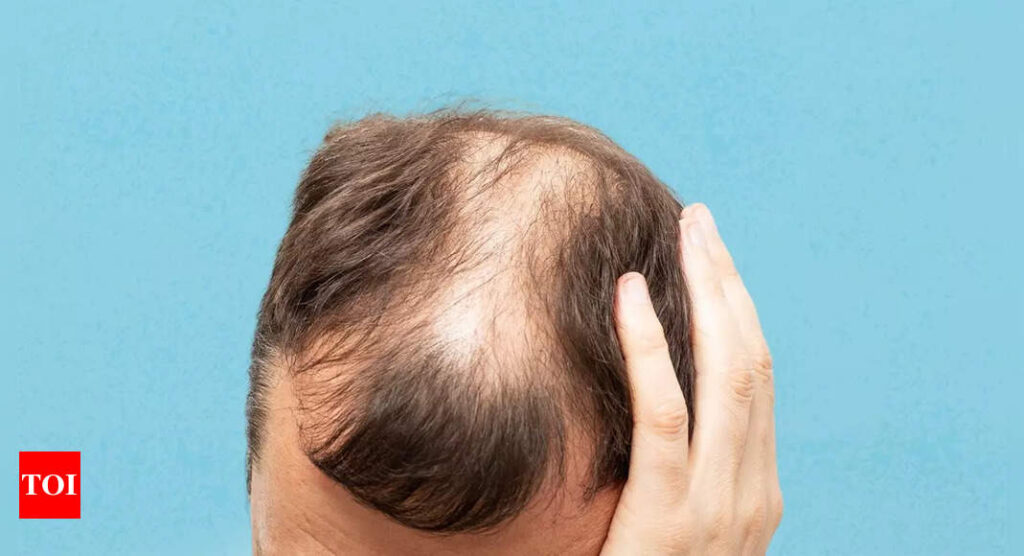
Premature baldness, also known as premature androgenetic alopecia, is when someone loses a significant amount of hair before the age of 30–35. It’s a common type of hair loss that can have a psychological impact.
Signs of premature baldness:
Although early balding is triggered by excessive hair-fall which leads to signifies hair-loss, there are several signs of the conditions, like:
Excessive hair shedding: You notice more loose hair on your pillow, in the shower, or in your hairbrush than usual. Healthy hair loss is usually around 50–100 strands per day.
Hair thinning: You notice thinning hair in different parts of your head. The scalp becomes more visible between your hair shafts.
Hair falling out in clumps: Hair loss is usually a gradual process, but sometimes there may be dramatic changes.
Receding hairline: Hair on the sides and front of the head may start to thin and move away from the face.
Widening part: The line where the hair splits on the top of the head may widen and pull apart.
More hair than normal falling out: You may notice more hairs than normal falling out and being left behind on your brush or comb and in the shower drain.
Hair pull test: Gently pull away from the scalp with light, even tension and count the hairs that get extracted. Consistently more than 10-15 hairs released indicates increased shedding.
Checking your hair under a strong light: You’ll be able to clearly see the top of your hair and identify how thin your hair has become.
Reasons of early balding:
Balding in men is mainly related to aging, heredity, and changes in the hormone testosterone. Following are the reasons of premature balding in men:
Age: The chances of developing male pattern baldness increase with age. About 25% of people assigned male at birth see the first signs of hair loss before age 21. By age 50, half experience hair loss, and about 70% will lose hair as they get older.
Hormones: Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a type of androgen. Androgens are a group of sex hormones that help people enter puberty and mature physically. Physical developments include hair growth on the face, scalp, chest, underarms and genitals. Medical experts and researchers think that there might be a link between DHT and your hair follicles shrinking.
Genetics: People assigned male at birth have one X chromosome they inherit from their mother and one Y chromosome they inherit from their father. The AR gene on your X chromosome tells your body how to make androgens. Your AR gene’s sensitivity helps determine male pattern baldness.
Other than these reasons, there are a few more causes that could trigger early balding in men:
Alopecia areata: An immune system-related condition that causes hair to fall out in small patches.
Telogen effluvium: A common type of hair loss that usually causes thinning at the temples and crown. It can be caused by stress, fever, surgery, and other factors.
Androgenetic alopecia: Also known as male and female pattern baldness, this hereditary condition can cause a receding hairline and hair loss from the crown and frontal scalp.
Traction alopecia: A common balding disorder for young women and girls with textured hair. It occurs when hair is pulled too tight and is pulled out of the follicle.
Trichotillomania: An irresistible urge to pull out hair that can lead to patches of baldness. It’s more common in children and young adults who are experiencing stress or anxiety.
Scalp infection: Chronic and untreated scalp infections can cause premature baldness.
Ways to treat early balding:
There are many treatments for early balding, including medications, cosmetic options, and at-home treatments:
Medications: The FDA-approved treatments for male pattern baldness are minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia):
Minoxidil: A topical solution that slows hair loss and can help some men grow new hair. It’s available over the counter, but hair loss returns when you stop using it.
Finasteride: An oral pill that slows hair loss by interfering with the production of testosterone linked to baldness. It’s only available with a prescription, and hair loss returns when you stop taking it.
Hair transplant: Skin grafts from areas of your body that contain healthy hair are taken and moved to the balding or thinning areas of your scalp. Side effects may include scalp pain and irritation, scarring, dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
Platelet-rich plasma: Blood is removed from your body, processed and injected into your scalp to stimulate hair growth. Side effects may include scalp pain and irritation, dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
There are some cosmetic options available as well that could help one with premature balding. One can use wigs, hairpieces, hair weaving, or camouflage sprays to hide hair loss. Synthetic wigs are cheaper and easier to maintain than real-hair wigs, but they can be itchy and hot.
How to know if your hair fall is normal?
Source Homevior.in